Jsp Save Request Parameter in Map and Restore Again
Servlets and JSP Pages All-time Practices
by Qusay H. Mahmoud
March 2003
Java Servlet technology and JavaServer Pages (JSP pages) are server-side technologies that have dominated the server-side Java technology market; they've go the standard style to develop commercial spider web applications. Java developers honey these technologies for myriad reasons, including: the technologies are fairly easy to learn, and they bring the Write In one case, Run Anywhere paradigm to web applications. More chiefly, if used effectively past following all-time practices, servlets and JSP pages aid dissever presentation from content. Best practices are proven approaches for developing quality, reusable, and easily maintainable servlet- and JSP-based web applications. For instance, embedded Java code (scriptlets) in sections of HTML documents tin issue in complex applications that are not efficient, and difficult to reuse, enhance, and maintain. Best practices tin change all that.
In this article, I'll nowadays important best practices for servlets and JSP pages; I assume that you take bones working knowledge of both technologies. This article:
- Presents an overview of Coffee servlets and JavaServer pages (JSP pages)
- Provides hints, tips, and guidelines for working with servlets and JSP pages
- Provides best practices for servlets and JSP pages
Overview of Servlets and JSP Pages
Like to Common Gateway Interface (CGI) scripts, servlets support a request and response programming model. When a client sends a asking to the server, the server sends the request to the servlet. The servlet then constructs a response that the server sends back to the client. Dissimilar CGI scripts, however, servlets run within the same procedure equally the HTTP server.
When a customer request is made, the service method is chosen and passed a request and response object. The servlet outset determines whether the request is a GET or Mail service operation. It then calls one of the following methods: doGet or doPost. The doGet method is called if the request is GET, and doPost is called if the request is Postal service. Both doGet and doPost take asking ( HttpServletRequest) and response ( HttpServletResponse).
In the simplest terms, then, servlets are Java classes that tin generate dynamic HTML content using print statements. What is of import to note about servlets, even so, is that they run in a container, and the APIs provide session and object life-cycle management. Consequently, when yous use servlets, y'all proceeds all the benefits from the Coffee platform, which include the sandbox (security), database access API via JDBC, and cross-platform portability of servlets.
JavaServer Pages (JSP)
The JSP technology--which abstracts servlets to a higher level--is an open up, freely available specification developed by Lord's day Microsystems every bit an alternative to Microsoft'southward Agile Server Pages (ASP) engineering science, and a cardinal component of the Java two Enterprise Edition (J2EE) specification. Many of the commercially available application servers (such every bit BEA WebLogic, IBM WebSphere, Live JRun, Orion, and and then on) support JSP engineering science.
How Do JSP Pages Work?
A JSP page is basically a web page with traditional HTML and bits of Java code. The file extension of a JSP folio is .jsp rather than .html or .htm, which tells the server that this page requires special handling that volition be accomplished by a server extension or a plug-in.
When a JSP page is called, information technology will be compiled (past the JSP engine) into a Java servlet. At this betoken the servlet is handled past the servlet engine, simply like whatsoever other servlet. The servlet engine then loads the servlet grade (using a grade loader) and executes it to create dynamic HTML to be sent to the browser, as shown in Effigy 1. The servlet creates any necessary object, and writes any object as a cord to an output stream to the browser.
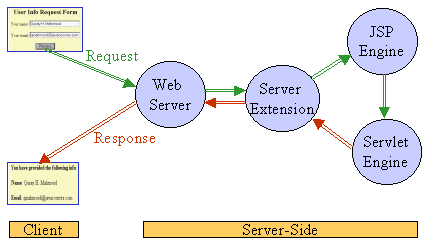
Figure 1: Request/Response catamenia calling a JSP page
The next time the page is requested, the JSP engine executes the already-loaded servlet unless the JSP page has changed, in which case it is automatically recompiled into a servlet and executed.
Best Practices
In this department, I present best practices for servlets and particularly JSP pages. The emphasis on JSP best practices is simply considering JSP pages seem to exist more widely used (probably because JSP technology promotes the separation of presentation from content). One best exercise that combines and integrates the utilize of servlets and JSP pages is the Model View Controller (MVC) design pattern, discussed afterward in this article.
- Don't overuse Java code in HTML pages: Putting all Coffee lawmaking straight in the JSP folio is OK for very simple applications. But overusing this feature leads to spaghetti code that is not easy to read and understand. One way to minimize Java code in HTML pages is to write separate Java classes that perform the computations. Once these classes are tested, instances tin be created.
- Choose the right include mechanism: Static data such as headers, footers, and navigation bar content is best kept in carve up files and not regenerated dynamically. Once such content is in divide files, they can be included in all pages using ane of the following include mechanisms:
- Include directive:
<%@ include file="filename" %> - Include activity:
<jsp:include page="page.jsp" flush="true" />
- Include directive:
- Don't mix business organization logic with presentation: For advanced applications, and when more code is involved, it's important not to mix business concern logic with front-end presentation in the same file. Separating concern logic from presentation permits changes to either side without affecting the other. However, product JSP code should be limited to front-end presentation. And then, how do you implement the concern logic part? That is where JavaBeans technology comes into play. This engineering is a portable, platform-contained component model that lets developers write components and reuse them everywhere. In the context of JSP pages, JavaBeans components contain business logic that returns data to a script on a JSP page, which in turn formats the data returned from the JavaBeans component for brandish by the browser. A JSP folio uses a JavaBeans component by setting and getting the properties that it provides. The benefits of using JavaBeans components to broaden JSP pages are:
- Reusable components: Dissimilar applications will be able to reuse the components.
- Separation of business logic and presentation logic: You can alter the way data is displayed without affecting business organization logic. In other words, web page designers can focus on presentation and Coffee developers tin can focus on business logic.
- Protects your intellectual holding by keeping source lawmaking secure.
- Use custom tags: Embedding bits of Java code (or scriptlets) in HTML documents may not be suitable for all HTML content developers, perhaps because they do not know the Coffee language and don't intendance to larn its syntax. While JavaBeans components can be used to encapsulate much of the Java lawmaking, using them in JSP pages still requires content developers to have some noesis of Java syntax.
JSP technology allows you to innovate new custom tags through the tag library facility. As a Coffee developer, you can extend JSP pages by introducing custom tags that can exist deployed and used in an HTML-like syntax. Custom tags also allow you to provide better packaging by improving the separation betwixt business logic and presentation logic. In addition, they provide a ways of customizing presentation where this cannot exist done easily with JSTL.
Some of the benefits of custom tags are:
- They can eliminate scriptlets in your JSP applications. Any necessary parameters to the tag tin exist passed as attributes or body content, and therefore no Coffee code is needed to initialize or set component properties.
- They have simpler syntax. Scriptlets are written in Java code, but custom tags can be used in an HTML-like syntax.
- They can improve the productivity of nonprogrammer content developers, by allowing them to perform tasks that cannot exist done with HTML.
- They are reusable. They save development and testing time. Scriptlets are not reusable, unless you call cut-and-paste "reuse."
In short, you tin use custom tags to achieve complex tasks the same way you lot utilize HTML to create a presentation.
The following programming guidelines are handy when writing custom tag libraries:
- Proceed information technology simple: If a tag requires several attributes, try to break it up into several tags.
- Make it usable: Consult the users of the tags (HTML developers) to accomplish a high degree of usability.
- Practice not invent a programming language in JSP pages: Exercise not develop custom tags that allow users to write explicit programs.
- Try not to re-invent the wheel: There are several JSP tag libraries available, such as the Jakarta Taglibs Project. Check to see if what y'all want is already available.
- Do non reinvent the wheel: While custom tags provide a way to reuse valuable components, they still demand to be created, tested, and debugged. In addition, developers ofttimes have to reinvent the wheel over and over once again and the solutions may non exist the most efficient. This is the problem that the JavaServer Pages Standard Tag Library (JSTL) solves, by providing a set up of reusable standard tags. JSTL defines a standard tag library that works the aforementioned everywhere, so you lot no longer have to iterate over collections using a scriptlet (or iteration tags from numerous vendors). The JSTL includes tags for looping, reading attributes without Coffee syntax, iterating over diverse data structures, evaluating expressions conditionally, setting attributes and scripting variables in a concise manner, and parsing XML documents.
- Use the JSTL Expression Language: Data to be passed to JSP pages is communicated using JSP scoped attributes and request parameters. An expression language (EL), which is designed specifically for page authors, promotes JSP scoped attributes as the standard way to communicate information from business logic to JSP pages. Annotation, still, that while the EL is a key aspect of JSP engineering, information technology is not a full general purpose programming linguistic communication. Rather, it is simply a information admission language, which makes it possible to hands admission (and manipulate) application data without having to use scriptlets or request-time expression values.
- Use filters if necessary: Ane of the new features of JSP technology is filters. If you ever come beyond a situation where you lot have several servlets or JSP pages that need to compress their content, you can write a unmarried compression filter and apply it to all resources. In Java BluePrints, for case, filters are used to provide the SignOn.
- Use a portable security model: Most application servers provide server- or vendor-specific security features that lock developers to a particular server. To maximize the portability of your enterprise awarding, utilize a portable spider web application security model. In the end, all the same, information technology's all virtually tradeoffs. For example, if y'all have a predefined set of users, you tin can manage them using course-based login or basic authentication. Just if you need to create users dynamically, y'all demand to apply container-specific APIs to create and manage users. While container-specific APIs are non portable, you can overcome this with the Adapter design pattern.
- Use a database for persistent information: You tin implement sessions with an
HttpSessionobject, which provides a unproblematic and user-friendly mechanism to shop information about users, and uses cookies to identify users. Use sessions for storing temporary data--so even if it gets lost, you'll be able to sleep at nighttime. (Session information is lost when the session expires or when the client changes browsers.) If you want to shop persistent data, utilise a database, which is much safer and portable across browsers. - Cache content: You should never dynamically regenerate content that doesn't alter between requests. You tin cache content on the client-side, proxy-side, or server-side.
- Employ connection pooling: I'd recommend using the JSTL for database access. But if y'all wish to write your own custom actions for database access, I'd recommend you lot utilise a connectedness pool to efficiently share database connections between all requests. However, notation that J2EE servers provide this under the covers.
- Cache results of database queries: If you desire to cache database results, do not use the JDBC's
ResultSetobject every bit the cache object. This is tightly linked to a connection that conflicts with the connection pooling. Copy the data from aResultSetinto an awarding-specific bean such every bitVector, or JDBC'southRowSets. - Adopt the new JSP XML syntax if necessary. This really depends on how XML-compliant y'all want your applications to be. There is a tradeoff here, however, because this makes the JSP more than tool-friendly, merely less friendly to the programmer.
- Read and apply the Enterprise BluePrints: Sun'due south Enterprise BluePrints provide developers with guidelines, patterns, and sample applications, such equally the Gamble Builder and Pet Shop. Overall, the J2EE BluePrints provide best practices and a set of design patterns, which are proven solutions to recurring problems in building portable, robust, and scalable enterprise Coffee applications.
The commencement include mechanism includes the content of the specified file while the JSP page is being converted to a servlet (translation phase), and the second include includes the response generated afterwards the specified page is executed. I'd recommend using the include directive, which is fast in terms of performance, if the file doesn't change often; and use the include action for content that changes oftentimes or if the page to be included cannot be decided until the main page is executed.
Another include mechanism is the <c:import> action tag provided past the JavaServer pages Standard Tag Library (JSTL). You can use this tag to bring in, or import, content from local and remote sources. Here are some examples:
<c:import url="./copyright.html"/> <c:import url="http://www.somewhere.com/how-do-you-do.xml"/> If yous utilise Enterprise JavaBeans (EJBs) components with your application, the business logic should remain in the EJB components which provide life-wheel management, transaction support, and multi-client access to domain objects (Entity Beans).
In JSP one.10, a page author must apply an expression <%= aName %> to admission the value of a system, as in the post-obit case:
<someTags:aTag attribute="<%= pageContext.getAttribute("aName") %>"> or the value of a custom JavaBeans component:
<%= aCustomer.getAddress().getCountry() %>
An expression language allows a page writer to access an object using a simplified syntax. For example, to access a uncomplicated variable, you tin can utilize something similar:
<someTags:aTag attribute="${aName}">
And to access a nested JavaBeans property, you would use something like:
<someTags.aTag attribute="${ aCustomer.address.state}"> If you've worked with JavaScript, you will experience right at home, because the EL borrows the JavaScript syntax for accessing structured information.
Integrating Servlets and JSP Pages
The JSP specification presents ii approaches for building web applications using JSP pages: JSP Model 1 and Model two architectures. These ii models differ in the location where the processing takes place. In Model 1 architecture, every bit shown in Figure 2, the JSP page is responsible for processing requests and sending dorsum replies to clients.
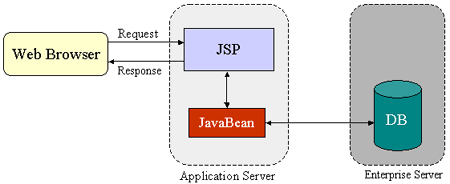
Figure 2: JSP Model 1 Architecture
The Model 2 architecture, equally shown in Effigy iii, integrates the use of both servlets and JSP pages. In this style, JSP pages are used for the presentation layer, and servlets for processing tasks. The servlet acts as a controller responsible for processing requests and creating any beans needed by the JSP page. The controller is as well responsible for deciding to which JSP folio to forward the asking. The JSP page retrieves objects created by the servlet and extracts dynamic content for insertion inside a template.
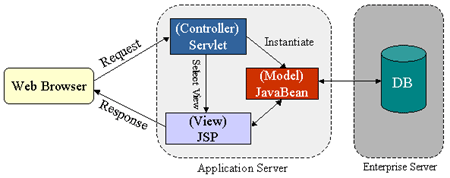
Figure 3: JSP Model 2 Architecture
This model promotes the use of the Model View Controller (MVC) architectural way pattern pattern. Annotation that several frameworks already be that implement this useful design design, and that truly divide presentation from content. The Apache Struts is a formalized framework for MVC. This framework is all-time used for complex applications where a unmarried request or form submission can result in substantially unlike-looking results.
Conclusion
Best practices -- which are proven solutions to recurring issues -- lead to college quality applications. This article presented several guidelines and best practices to follow when developing servlet- and JSP-based web applications.
Keep an eye on servlets and JSP technologies, because several exciting things are in the works. JavaServer Faces (JFC), for example, a Java Customs Procedure effort that aims to ascertain a standard web application framework, will integrate nicely with Apache Struts.
For more data
- Tomcat
- Servlets
- JavaServer Pages
- Enterprise BluePrints
- Apache Struts
- Code Conventions for the JavaServer Pages Engineering science Version 1.ten Language
- Java Server Faces (JSF)
Acknowledgments
Special thanks to Gregory Murray of Sun Microsystems, whose feedback helped me improve this article.
Well-nigh the author
Qusay H. Mahmoud provides Java consulting and preparation services. He has published dozens of articles on Java, and is the writer of Distributed Programming with Java (Manning Publications, 1999) and Learning Wireless Java (O'Reilly, 2002).
Source: https://www.oracle.com/technical-resources/articles/javase/servlets-jsp.html
0 Response to "Jsp Save Request Parameter in Map and Restore Again"
Post a Comment